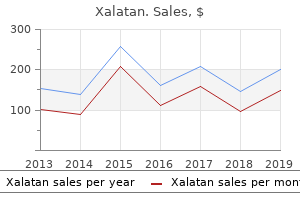
Xalatan
"Purchase xalatan 2.5 ml on-line, symptoms ruptured ovarian cyst".
By: B. Kaffu, M.B. B.CH. B.A.O., Ph.D.
Clinical Director, University of Utah School of Medicine
Practice Parameter update: Management issues for women with epilepsy-Focus on pregnancy (an evidence-based review): Teratogenesis and perinatal outcomes medications 512 purchase 2.5 ml xalatan free shipping. Report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee and Therapeutics and Technology Assessment Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology and American Epilepsy Society medicine 906 xalatan 2.5ml mastercard. Steering Committee on Quality Improvement and Management treatment vaginitis cheap 2.5 ml xalatan mastercard, Subcommittee on Febrile Seizures medications that raise blood sugar buy xalatan online. Febrile Seizures: Clinical proactive guideline for the long-term management of the child with simple febrile seizures. Vasopressin v(2) receptor blockade with tolvaptan versus fluid restriction in the treatment of hyponatremia. Gabapentin in the treatment of fibromyalgia: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial. Psychological interventions for major depression in primary care: a meta-analytic review of randomized controlled trials. Guideline for the management of fibromyalgia syndrome pain in adults and children. Comparative efficacy and acceptability of 12 newgeneration antidepressants: a multiple-treatments meta-analysis. Requests for continuing therapy that were approved by a previous Health Plan will be honored for at least 30 days upon receipt of documentation demonstrating that approval 7. Milnacipran for the treatment of fibromyalgia in adults: a 15-week, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multiple-dose clinical trial. Comparative Effectiveness of SecondGeneration Antidepressants in the Pharmacologic Treatment of Adult Depression. Comparative benefits and harms of secondgeneration antidepressants: background paper for the American College of Physicians. A doubleblind comparison of the efficacy and safety of milnacipran and fluoxetine in depressed inpatients. Meta-analysis of major depressive disorder relapse and recurrence with second-generation antidepressants. A double-blind six months comparative study of milnacipran and clomipramine in major depressive disorder. Sechter D, Vandel P, Weiller E, Pezous N, Cabanac F, Tournoux A; study co-coordinators. A comparative study of milnacipran and paroxetine in outpatients with major depression. Double-blind study of the efficacy and safety of milnacipran and imipramine in elderly patients with major depressive episode. Mirtazapine versus other antidepressants in the acute-phase treatment of adults with major depression: systematic review and metaanalysis. If the patient has not lost 4% of baseline body weight, Saxenda should be discontinued because it is unlikely that the patient will achieve and sustain clinically meaningful weight loss with continued treatment. If the patient cannot tolerate an increased dose during dose escalation, consider delaying dose escalation for one week. If the 3 mg daily dose is not tolerated, discontinue use as efficacy has not been established at lower doses. Tertiary hyperparathyroidism in post-kidney transplant patients not receiving dialysis All other indications are considered experimental/investigational and are not a covered benefit. Primary Hyperparathyroidism Authorization of 12 months may be granted for the treatment of primary hyperparathyroidism in a member who is not able to undergo parathyroidectomy and has a serum calcium level (corrected for albumin) greater than or equal to 8. Tertiary Hyperparathyroidism in Post-Kidney Transplant Patients Not Receiving Dialysis Authorization of 12 months may be granted for the treatment of tertiary hyperparathyroidism in a member who has had a kidney transplant, is not receiving dialysis, and has a serum calcium level (corrected for albumin) greater than or equal to 8. Parathyroid Carcinoma Authorization of 12 months may be granted for the treatment of parathyroid carcinoma in a member who has a serum calcium level (corrected for albumin) greater than or equal to 8. A randomized study evaluating cinacalcet to treat hypercalcemia in renal transplant recipients with persistent hyperparathyroidism.
Sensitive periods in epigenetics: bringing us closer to complex behavioral phenotypes symptoms of mono buy xalatan with paypal. Maternal care 3 medications that affect urinary elimination generic 2.5 ml xalatan overnight delivery, hippocampal glucocorticoid receptors medications qhs buy 2.5ml xalatan amex, and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal responses to stress symptoms 16 weeks pregnant discount xalatan 2.5 ml otc. Nongenomic transmission across generations of maternal behavior and stress responses in the rat. Conserved epigenetic sensitivity to early life experience in the rat and human hippocampus. The dexamethasone/corticotropin-releasing factor test in men with major depression: role of childhood trauma. Pituitary-adrenal and autonomic responses to stress in women after sexual and physical abuse in childhood. Cerebrospinal fluid corticotropin-releasing factor and perceived early-life stress in depressed patients and healthy control subjects. Suicidal behavior and severe neuropsychiatric disorders following glucocorticoid therapy in primary care. Differential glucocorticoid receptor exon 1(b), 1(c), and 1(h) expression and methylation in suicide completers with a history of childhood abuse. Epigenetic regulation of the glucocorticoid receptor in human brain associates with childhood abuse. Transgenerational impact of intimate partner violence on methylation in the promoter of the glucocorticoid receptor. Childhood adversity and epigenetic modulation of the leukocyte glucocorticoid receptor: preliminary findings in healthy adults. Differential expression of glucocorticoid receptor transcripts in major depressive disorder is 24. Serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor, depression, and antidepressant medications: meta-analyses and implications. Sustained hippocampal chromatin regulation in a mouse model of depression and antidepressant action. Neurotrophin receptor activation and expression in human postmortem brain: effect of suicide. Transcriptional profiling reveals evidence for signaling and oligodendroglial abnormalities in the temporal cortex from patients with major depressive disorder. Genome-wide expression analysis detects eight genes with robust alterations specific to bipolar I disorder: relevance to neuronal network perturbation. Alternative splicing, methylation state, and expression profile of tropomyosin-related kinase B in the frontal cortex of suicide completers. Early childhood adversities and trajectories of psychiatric problems in adoptees: evidence for long lasting effects. Childhood adversities, interpersonal difficulties, and risk for suicide attempts during late adolescence and early adulthood. Risk factors and life processes associated with the onset of suicidal behaviour during adolescence and early adulthood. Childhood trajectories of anxiousness and disruptiveness explain the association between early-life adversity and attempted suicide. Assessing the validity of bloodbased gene expression profiles for the classification of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder: a preliminary report. Disease-associated epigenetic changes in monozygotic twins discordant for schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Functional annotation of the human brain methylome identifies tissue-specific epigenetic variation across brain and blood. September 2014 Neurobiological Risk Factors for Suicide Insights from Brain Imaging Elizabeth T. Evidence acquisition: A PubMed search was conducted and articles published before March 2014 were reviewed that compared individuals who made suicide attempts to those with similar diagnoses who had not made attempts or to healthy comparison subjects. Articles on adults with suicidal ideation and adolescents who had made attempts, or with suicidal ideation, were also included. Reviewed imaging modalities included structural magnetic resonance imaging, diffusion tensor imaging, single photon emission computed tomography, positron emission tomography, and functional magnetic resonance imaging. Evidence synthesis: Although many studies include small samples, and subject characteristics and imaging methods vary across studies, there were convergent findings involving the structure and function of frontal neural systems and the serotonergic system.
A meta-analysis of 40 group treatment studies suggested moderate efficacy for group therapy treatment pink eye order 2.5ml xalatan free shipping, with those studies that provided 1-year follow-up data reporting that improvement was typically maintained (680) symptoms ulcerative colitis discount xalatan 2.5ml overnight delivery. There is some evidence that group treatment programs that include dietary counseling and management as part of the program are more effective than those that do not (208) and that more frequent visits symptoms xanax addiction buy line xalatan. A systematic study of family therapy for adolescents with bulimia nervosa is currently under way (89) symptoms 2 days after ovulation order 2.5 ml xalatan overnight delivery, but no results have been reported yet. Family therapy should be considered whenever possible, especially for adolescents who still live with their parents, older patients with ongoing conflicted interactions with parents, or patients with marital discord. A review of self-help treatments with or without guidance by a professional has recently been published (690). Although such techniques are not yet sufficiently developed to recommend their acceptance as a primary treatment strategy, developments in this area may prove of great importance in providing treatment to patients who otherwise might not have access to adequate care. Medications a) Antidepressants Early observations that individuals with bulimia nervosa exhibit an elevated lifetime prevalence of mood disorders, together with an elevated prevalence of mood disorders in their first-degree relatives, prompted initial trials of antidepressants for the acute treatment of bulimia nervosa (233). In these trials, antidepressants appeared to be effective for bulimia nervosa regardless of whether or not the patient was clinically depressed. Subsequent randomized trials confirmed that nondepressed patients responded to these medications and that the baseline presence of depression was not a predictor of medication response (234, 235, 697, 698). Treatment with bupropion was also efficacious (181), but its use is not recommended because of the association between bupropion treatment and seizures in purging bulimic patients. The results of one study (709) suggest that patients with atypical depression and bulimia nervosa may preferentially respond to phenelzine in comparison with imipramine. The first multicenter fluoxetine study (230) demonstrated that 60 mg/day was clearly superior to 20 mg/day on most variables, and in a second study (224) all subjects receiving active medication started with 60 mg/day. A third trial used 60 mg/day as a maintenance therapy, but the dropout rate from the study was very high (226). The medication was surprisingly well tolerated at this dosage, and many clinicians initiate treatment for bulimia nervosa with fluoxetine at a higher dosage, titrating downward if necessary to manage side effects. Three trials have examined the effectiveness of antidepressant maintenance therapy. One trial with fluvoxamine (701) demonstrated an attenuated relapse rate versus placebo in patients with bulimia nervosa who were on a maintenance regimen of the medication after leaving an inpaTreatment of Patients With Eating Disorders 83 Copyright 2010, American Psychiatric Association. However, in the continuation arm of a clinical trial with desipramine (240), 29% of the patients entering that phase experienced a relapse within 4 months. A 1-year maintenance trial using fluoxetine or placebo found evidence for a lower relapse rate on active drug, but the dropout rate was quite high in both treatment arms (226). An open-label trial found evidence that fluoxetine could be effective in adolescents (225). The results were somewhat inconsistent in that one study found medication to be quite useful, whereas the other found low rates of response and high dropout rates. Fenfluramine has now been taken off the market because of links between its use (mainly in combination with phentermine) and cardiac valvular abnormalities. Lithium may occasionally be used concurrently for the treatment of co-occurring conditions. The results consistently show that the medication is not superior to placebo in reducing bulimic symptoms (699, 704, 707). However, there have been mixed reports concerning the risk of hepatotoxicity with the use of high dosages of naltrexone (705, 706, 718). In a randomized controlled trial, carbamazepine showed efficacy in only one patient, and that patient had a history of bipolar disorder (720). Combinations of psychosocial and medication treatments the relative efficacy of psychotherapy, medication, or both in the treatment of bulimia nervosa has been examined in six studies. In the first study (253), intensive group cognitive psychotherapy (45 hours of therapy over 10 weeks) was superior to imipramine alone in reducing binge eating/purging and depressive symptoms. Some advantage was also seen for combination therapy on some variables, such as dietary restraint.
Bussolotti D symptoms lead poisoning proven xalatan 2.5ml, Fernandez-Aranda F treatment broken toe discount xalatan online amex, Solano R treatment depression purchase xalatan 2.5 ml on-line, Jimenez-Murcia S symptoms 0f brain tumor purchase xalatan 2.5ml free shipping, Turon V, Vallejo J: Marital status and eating disorders: an analysis of its relevance. Okamoto A, Yamashita T, Nagoshi Y, Masui Y, Wada Y, Kashima A, Arii I, Nakamura M, Fukui K: A behavior therapy program combined with liquid nutrition designed for anorexia nervosa. Beumont P, Carney T: Can psychiatric terminology be translated into legal regulation Strober M: Managing the chronic, treatment-resistant patient with anorexia nervosa. Fennig S, Fennig S, Roe D: Physical recovery in anorexia nervosa: is this the sole purpose of a child and adolescent medical-psychiatric unit Gowers S, Bryant-Waugh R: Management of child and adolescent eating disorders: the current evidence base and future directions. Fernandez-Aranda F, Bel M, Jimenez S, Vinuales M, Turon J, Vallejo J: Outpatient group therapy for anorexia nervosa: a preliminary study. Bloom C, Gitter A, Gutwill S: Eating Problems: A Feminist Psychoanalytic Treatment Model. Dare C, Crowther C: Living dangerously: psychoanalytic psychotherapy of anorexia nervosa, in Handbook of Eating Disorders: Theory, Treatment, and Research. Thompson-Brenner H, Westen D: A naturalistic study of psychotherapy for bulimia nervosa, part 2: therapeutic interventions and outcome in the community. Yager J: Management of patients with intractable eating disorders, in Eating Disorders and Obesity: A Comprehensive Handbook, 2nd ed. Strober M, Pataki C, Freeman R, DeAntonio M: No effect of adjunctive fluoxetine on eating behavior or weight phobia during the inpatient treatment of anorexia nervosa: an historical case-control study. Fassino S, Leombruni P, Daga G, Brustolin A, Migliaretti G, Cavallo F, Rovera G: Efficacy of citalopram in anorexia nervosa: a pilot study. American Psychiatric Association, American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry: Physicians Med Guide: the use of medication in treating child and adolescent depression: information for physicians. Paper presented at the Broadening the Horizon of Atypical Antipsychotic Applications symposium, New York, 2004. Bosanac P, Norman T, Burrows G, Beumont P: Serotonergic and dopaminergic systems in anorexia nervosa: a role for atypical antipsychotics Thompson-Brenner H, Glass S, Westen D: A multidimensional meta-analysis of psychotherapy for bulimia nervosa. Petrucelli J, Stuart C: Hungers and Compulsions: the Psychodynamic Treatment of Eating Disorders and Addictions. Schmidt U, Tiller J, Treasure J: Self-treatment of bulimia nervosa: a pilot study. Thiels C, Schmidt U, Treasure J, Garthe R, Troop N: Guided self-change for bulimia nervosa incorporating use of a self-care manual. Milano W, Petrella C, Sabatino C, Capasso A: Treatment of bulimia nervosa with sertraline: a randomized controlled trial.
Rhetorical figures force a message recipient to create a conceptual connection as opposed to having the connection literally provided to him or her medications 222 cheap 2.5 ml xalatan with mastercard. It is this creative connection that makes two otherwise disparate concepts ironic medications safe in pregnancy generic 2.5ml xalatan with mastercard, humorous medications an 627 discount 2.5 ml xalatan, or entertaining medicine 93 quality 2.5 ml xalatan. In this sense, rhetorical figures force the recipient to be a co-producer of message meaning. It is not surprising then to find that the individual elaborates more or finds the message to be more interesting and memorable. New Product Development We previously alluded to the fact that consumer creativity may have marketing benefits, particularly in the area of new product development. Most new product failures are ultimately a failure to adequately understand and meet the needs of some customer base. It is therefore somewhat perplexing that consumer creativity has received limited attention as a possible source of new product ideas (for exceptions see Dahl & Moreau, 2002; Prahalad & Ramaswamy, 2000; von Hippel, Thomke, & Sonnack, 1999). We consider some of the major challenges facing the new product development process and relate these to issues discussed earlier in conjunction with consumer creativity. Hopefully, this discussion will provide new vantage points on the role and application of consumer creativity to the new product development process. Lead Users VonHippel (1986) discusses the importance of lead users in the product development process. Lead users are consumers who face a need ahead of the mainstream market, and in so doing, they often create their own solutions. These instances of creative consumption regularly occur well before there is any commercial product available to address the given need. For this reason, lead users are often an invaluable source of new product ideas and improvements. Their value may also stem from the exploration and incubation stages of the creative process. Recall that individuals must often struggle with multiple potential approaches to a problem or issue, and that a period of apparent idle time often precedes creative insight. The very nature of lead users puts them in a position to benefit the most from the way the creative process unfolds. When lead users encounter a problem with a particular product, they are likely to struggle with it repeatedly over multiple instances and settings. As with any creative breakthrough, the moment of insight is likely to reflect a prolonged period of exposure to the product and its problems. Another interesting issue related to lead users revolves around the question of intrinsic motivation. We have previously reviewed the benefits of intrinsic motivation to the creative process, but it is interesting to consider this issue in the context of lead users. Individuals hold jobs for any number of reasons, with some people deriving great personal satisfaction from their work and others seeing a job as little more than a paycheck. This range of work orientations is likely to have a pronounced effect on the creativity of lead users. Individuals who interact with products because they must in order to do their job are likely to be less creative then individuals whose interaction with products is derived from an inherent interest in their work. While a great deal of research effort has been expended in marketing and management to understand the impact work orientations on job performance, these findings have not been extended to the issue of creativity, lead users, or new product development. Affect New product development (and the workplace more generally) may provide an interesting context to examine the role of affect on creativity. In support of this premise, Amabile and Conti (1999) describe how positive workplace environments foster creativity, whereas workplace creativity declines during periods of downsizing. But many creative innovations are as driven by tension and apprehension as by interest and enjoyment (sometimes at the same time). This raises the interesting question as to when stress (a negative affective state) is actually conducive to creativity. When stressors are interpreted as challenges they tend to enhance creativity while those that are interpreted as excess burdens tend to impede it (Amaible et al. Aside from this research, the issue of how negative affective states impact workplace creativity, particularly in the creation of new products, remains largely unexamined. Metaphor the potential of incorporating metaphor into new product design is not something most researchers consider.
Purchase generic xalatan on line. Howie Mandel Talks About Living With OCD | 20/20 | ABC News.