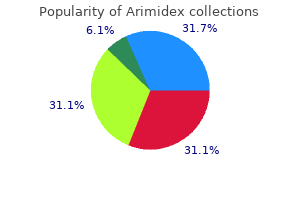
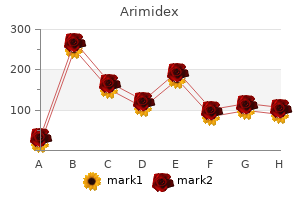
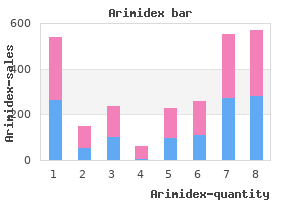
Arimidex
"Proven arimidex 1mg, menstruation 6 weeks after giving birth".
By: L. Denpok, MD
Professor, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania
Sialolithiasis refers to the formation of calculi within the salivary gland pregnancy 0-9 weeks purchase arimidex with a visa, and sialadenitis refers to the inflammation that occurs when the gland is obstructed women's health center university of arizona 1mg arimidex with visa. Diagnosis of sialolithiasis can be confirmed by point-of-care ultrasound performed by emergency physicians menopause medscape purchase arimidex 1mg online. Bedside ultrasound is a rapid pregnancy 01 discount 1mg arimidex with amex, non-ionizing, first-line method to confirm diagnosis when suspicion of other complications such as abscess is low. The patient followed up with otolaryngology as an outpatient three days later with subsequent removal of the sialolith 14 days later in the operating room. Diseases of the submandibular gland as demonstrated using high-resolution ultrasound. She noted that the ankle hurt with even light touch and the pain was unrelieved with ibuprofen. She was seen in the emergency department for this condition the day prior with a negative radiograph, but she returned because of increased ongoing pain. The patient received a diagnosis of posterior tibial tendon tenosynovitis with posterior tibial nerve neuralgia. She had complete resolution of her symptoms at eight weeks, at which time she resumed full activity. The mainstay of treatment includes anti-inflammatory medications, activity modification, foot orthosis, and physical therapy to improve stability and inhibit overpronation. Posterior tibial tendon tenosynovitis is an inflammatory condition affecting healthy young athletes and can be associated with posterior tibial nerve hyperesthesia. This image adds to the growing literature describing the use of ultrasound for evaluation of posterior tibial tendon and helps broaden the differential diagnosis related to ankle pain by emergency department providers. This image helps to highlight tenosynovitis of the posterior tibial tendon within the differential diagnosis and emphasizes the value of point-of-care ultrasound in establishing the diagnosis. Diagnostic efficacy of ultrasonography in stage I posterior tibial tendon dysfunction: sonographic-surgical correlation. Tibialis posterior in health and disease: a review of structure and function with specific reference to electromyographic studies. Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction: its association with seronegative inflammatory disease. Computed tomography of the head without contrast showed no acute intracranial abnormality. However, even at higher ends of the therapeutic range, patients can experience adverse effects such as diplopia, blurred vision, nystagmus, or ataxia. Carbamazepine is an anticonvulsant used to treat epilepsy, bipolar disorder and trigeminal neuralgia. Massive overdose with controlled-release carbamazepine resulting in delayed peak serum concentrations and life-threatening toxicity. Over two liters of urine were drained initially, and the urine collection bag was subsequently emptied. Previous recommendations have suggested gradual drainage of an obstructed bladder, for instance by intermittent catheter clamping, to avoid complications of hematuria, hypotension, and postobstructive diuresis, although the value of this practice is debatable. A systematic literature review of related studies published from 1920 to 1997 found no cases of hematuria severe enough to necessitate further invasive therapy, such as bladder irrigation or blood transfusion. Hematuria is demonstrated after bladder decompression, although the patient suffered no adverse complications. Although complications of rapid bladder decompression can occur very rarely, evidence from literature reviews and controlled trials supports rapid and complete emptying of the obstructed urinary bladder. Management of urinary retention: rapid versus gradual decompression and risk of complications. Significant upper urinary tract hematuria as a rare complication of high-pressure chronic retention of urine following decompression: a case report. The patient subsequently underwent an endoscopic retrograde cholangio-pancreatography with removal of one stone and sphincterotomy. All symptoms improved, and the patient was discharged home with appropriate follow up. Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography illustrating a persistent distal filling defect (arrow) of the common bile duct near the ampulla of vater suspicious for retained stone with slightly dilated common bile duct. It is the next appropriate step for patients with low to moderate risk of choledocolithiasis.
Syndromes
- Colorectal cancer
- Decreased ability to fight infection
- Unexplained pelvic pain (usually only done after ultrasound)
- Low blood pressure -- develops rapidly
- Damage to nearby organs
- Ten days before the surgery, your child may be asked to stop taking aspirin, ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin), naproxen (Aleve, Naprosyn), warfarin (Coumadin), and other drugs like these.
- Did it begin suddenly?
- Drowsiness
- Medicines to help your bladder contract and empty. These are called anticholinergic drugs. Possible side effects include slowed heart rate, low blood pressure, increased thirst, and constipation.
- Aging changes in the face
Neuronal hyperexcitability has been suggested as a contributing factor to the chronic pain women's health clinic jackson hole buy generic arimidex on-line. Treatment of central pain in patients with traumatic brain injury is challenging pregnancy recipes cheap arimidex master card, because most of these patients are also suffering from cognitive deficits and emotional distress women's health birth control article cheap arimidex online, and neuropathic pain may overlap with pain of psychogenic origin menstrual abnormalities generic arimidex 1mg fast delivery. It was previously called thalamic pain according to the typical location of the lesion, but it can also be due to cortical (parietal cortex), subcortical, internal capsule (posterior limb), or brainstem lesion. In the majority of patients, central poststroke pain is a contralateral hemi-pain, not always including the face, but it may also be restricted to part of the upper or lower extremity. The most common pain quality is Central Neuropathic Pain 193 hematomas usually present with headache and progressive neurological symptoms, but central neuropathic pain is an uncommon symptom in these cases. The cornerstones of the diagnosis are a detailed history of development of symptoms and relieving and aggravating factors, and a careful neurological examination including sensory testing to touch, pinprick, cold, warmth, and vibration. Abnormal sensory findings suggest the possibility of neuropathic pain, and other neurological findings help to localize the site of the lesion. It is important to keep in mind that the region of sensory abnormalities may be larger than the painful region (Case 2). Typical neurological findings referring to a central neurological lesion are a positive Babinski sign, accelerated tendon reflexes, and spasticity. Careful clinical examination is usually sufficient for this process, such as diagnosing musculoskeletal pain or pain due to local infection. Diagnostic studies, such as neuroimaging and cerebrospinal fluid analysis, may provide useful information in reaching an accurate diagnosis, but they may not be available. In such conditions, recognition of the clinical features of the causative diseases is very useful. The decision as to the use of limited resources and selection of patients for referral is based on the possibilities of treatment of the causative disease, such as with neurosurgery. Spinal and cerebral abscesses, spinal traumas with partial cord lesion, and spinal tumors are examples of conditions with radically improved prognosis with active surgical treatment. Cerebral abscess should be suspected if a patient has fever and progressive neurological symptoms (in cerebral abscess contralateral symptoms, and in spinal abscess sensory and motor deterioration below the level of the abscess). History of trauma before the onset of weakness of the limbs and sensory changes, including central pain, is suggestive of partial cord lesion. If there is an unstable lesion of the vertebral column, quick stabilizing surgery may prevent complete paralysis, and the same is true with laminectomies in spinal contusion with partial paresis. Slowly progressive paraparesis and sensory changes may be caused by a spinal tumor. The final prognosis depends on the histology of the tumour and the severity of the symptoms before surgery. The first line of therapy, after a thorough assessment, is information and education, for both the patient and the family. The character of the pain, the disease causing it, and the possibilities for pain relief need to be explained to the patient and the family. As symptomatic treatment of central neuropathic pain is less successful than treatment of peripheral neuropathic pain, giving thorough information may be the best way to help the patient. Similarly to peripheral neuropathic pain, antidepressants and anticonvulsants are used for symptomatic treatment of central neuropathic pain. It is started with 1025 mg in the evening, and the dose is escalated by 1025 mg steps to 50150 mg/day depending on the extent of side effects. Difficulties in urination, constipation, dry mouth, and dizziness are typical side effects, which may prevent further dose escalation. If amitriptyline is intolerable or ineffective, carbamazepine can be tried instead. If side effects (dizziness, headache, ataxia, or nystagmus) appear, the dose should be reduced. Pregabalin has been shown effective for spinal cord injury pain, but it is not available in every country.
Severely weak patients may have to "stack" in order to maintain head control and find the right balance in their trunk in supported sitting pregnancy and caffeine buy arimidex with amex. The head can drop quickly and when flexed forward menstrual not stopping buy discount arimidex, it can be very difficult to lift the head back up pregnancy and headaches discount generic arimidex uk. An inability to quickly recover and lift the head back up can also lead to airway blockage womens health institute peoria il cheap arimidex. Sitting Active knee extension may be observed but it should be determined if it is recoil from active knee flexion only. Lower extremity contractures can limit their ability to tolerate certain sitting positions (crossed leg, long sitting, etc. Sitting balance and weight shifts are often difficult due to diminished protective and righting reactions secondary to weakness. Transitions from sitting to lying can be difficult and many are at risk of falling from a lack of control. Some will exhibit a controlled flopping forward or will turn to prone in order to transition from sitting to lying. In transitions from lying to sitting, a patient may also have to move into prone or quadruped to push up. Some patients state they are unable to sit up without being able to move their legs off the edge of their bed for momentum to assist. Lifting the head off the bed (from either prone or supine) is often difficult and you may see neck protraction or side flexion to accomplish this as well as excessive arm or trunk movements. When rolling, it may be difficult to free the arms to move them out from under the body. When in supine and lifting their leg(s) or bringing knee(s) to chest, patients may use their arms to help, externally rotate, roll to their side to create momentum, or use two legs to brace and support movement. Lower extremity contractures of the knees and hips can impact the ability to straighten the legs out, externally rotate or tolerate the prone position. When in prone, patients may require the use of their arms to support their head upright when propped. Severely weak patients may require external support of the arms or legs to promote any active movement and eliminate friction from the surface Neck contractures may also limit the ability to rotate their head in either direction or maintain midline. Kneeling & Crawling Patients may have difficulty holding their head up when on their hands and knees and when attempting to crawl. Proximal weakness creates great difficulty when pulling the Lying 14 leg forward to crawl and may require an alternative crawling pattern to accomplish any locomotion. Transitions from kneeling to standing may require the use of their arms on their body (Gowers maneuver), furniture, or external support. The patient may have to lean their trunk on the support surface as well to help with this transition. If a patient has difficulty standing unsupported, you may see them leaning their trunk on a support surface to stand. Squatting can be very difficult and may require the use of arm support or furniture to accomplish. Some may only be able to unlock their knees minimally or flex their trunk/hips forward to attempt a squat. Standing posture may include a wide-base of support, knee hyperextension, increased lumbar lordosis, and/or Achilles tendon tightness. A waddling, Trendelenburg gait pattern may be exhibited with a wide-base, increased external rotation, knee hyperextension, minimal heel strike, and increased foot pronation. Jumping with both feet simultaneously can be challenging as well as landing safely without falling. Patients may require assistance or use one or two railings to ascend/descend stairs. Different patterns may include side-stepping facing the railing, step-to, or alternating steps. In order to increase upper extremity function, patients may use their fingers to climb up their body, or may flex their body to bring it closer to their hands. When writing, patients may need to move and adjust the position of their hand or the paper to maintain this ability.
Paragraph (c) of this section sets forth the qualifications and aids to interpretation for the terms used in the Table womens health editorial calendar order generic arimidex from india. Conditions and injuries that do not meet the terms of the qualifications and aids to interpretation are not within the Table women's health big book of exercises results cheapest generic arimidex uk. Paragraph (d) of this section sets forth a glossary of terms used in paragraph (c) breast cancer 6 months to live order arimidex 1 mg visa. Vaccine Time period for first symptom or manifestation of onset or of Illness women's health newsletter 1mg arimidex with amex, disability, injury significant aggravation after or condition covered vaccine administration 4 hours. Anaphylaxis bacteria, extracted or partial cell pertussis bacteria, or specific pertussis antigen(s). Vaccine-Strain Measles Viral Disease in an immunodeficient recipient -Vaccine-strain virus identified Not applicable. Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) vaccines Time period for first symptom or manifestation of onset or of Illness, disability, injury significant aggravation after or condition covered vaccine administration A. Disseminated varicella vaccine-strain viral disease -Vaccine-strain virus identified Not applicable. Guillain-Barrй Syndrome 3-42 days (not less than 3 days and not more than 42 days). The following qualifications and aids to interpretation shall apply to , define and describe the scope of, and be read in conjunction with paragraphs (a), (b), and (d) of this section: (1) Anaphylaxis. Anaphylaxis is an acute, severe, and potentially lethal systemic reaction that occurs as a single discrete event with simultaneous involvement of two or more organ systems. Death, if it occurs, usually results from airway obstruction caused by laryngeal edema or bronchospasm and may be associated with cardiovascular collapse. Other significant clinical signs and symptoms may include the following: Cyanosis, hypotension, bradycardia, tachycardia, arrhythmia, edema of the pharynx and/or trachea and/or larynx with stridor and dyspnea. There are no specific pathological findings to confirm a diagnosis of anaphylaxis. A vaccine recipient shall be considered to have suffered an encephalopathy if an injury meeting the description below of an acute encephalopathy occurs within the applicable time period and results in a chronic encephalopathy, as described in paragraph (d) of this section. A vaccine recipient shall be considered to have suffered encephalitis if an injury meeting the description below of acute encephalitis occurs within the applicable time period and results in a chronic encephalopathy, as described in paragraph (d) of this section. Encephalitis is indicated by evidence of neurologic dysfunction, as described in paragraph (c)(3)(i)(A) of this section, plus evidence of an inflammatory process in the brain, as described in paragraph (c)(3)(i)(B) of this section. This is characterized by a sudden onset of abdominal pain that may be manifested by anguished crying, irritability, vomiting, abdominal swelling, and/or passing of stools mixed with blood and mucus. Chronic arthritis is defined as persistent joint swelling with at least two additional manifestations of warmth, tenderness, pain with movement, or limited range of motion, lasting for at least 6 months. This term is defined as dysfunction limited to the upper extremity nerve plexus. A deep, steady, often severe aching pain in the shoulder and upper arm usually heralds onset of the condition. The pain is typically followed in days or weeks by weakness in the affected upper extremity muscle groups. Sensory loss may accompany the motor deficits, but is generally a less notable clinical feature. The neuritis, or plexopathy, may be present on the same side or on the side opposite the injection. A vaccine recipient shall be considered to have suffered brachial neuritis as a Table injury if such recipient manifests all of the following: (i) Pain in the affected arm and shoulder is a presenting symptom and occurs within the specified time-frame; (ii) Weakness; (A) Clinical diagnosis in the absence of nerve conduction and electromyographic studies requires weakness in muscles supplied by more than one peripheral nerve. This term is defined by the presence of clinical manifestations, such as petechiae, significant bruising, or spontaneous bleeding, and by a serum platelet count less than 50,000/mm3 with normal red and white blood cell indices. Thrombocytopenic purpura does not include cases of thrombocytopenia associated with other causes such as hypersplenism, autoimmune disorders (including alloantibodies from previous transfusions) myelodysplasias, lymphoproliferative disorders, congenital thrombocytopenia or hemolytic uremic syndrome. Thrombocytopenic purpura does not include cases of immune (formerly called idiopathic) thrombocytopenic purpura that are mediated, for example, by viral or fungal infections, toxins or drugs. Thrombocytopenic purpura does not include cases of thrombocytopenia associated with disseminated intravascular coagulation, as observed with bacterial and viral infections. Viral infections include, for example, those infections secondary to Epstein Barr virus, cytomegalovirus, hepatitis A and B, human immunodeficiency virus, adenovirus, and dengue virus.
Purchase arimidex from india. Medicare & You: Women's health.